Description
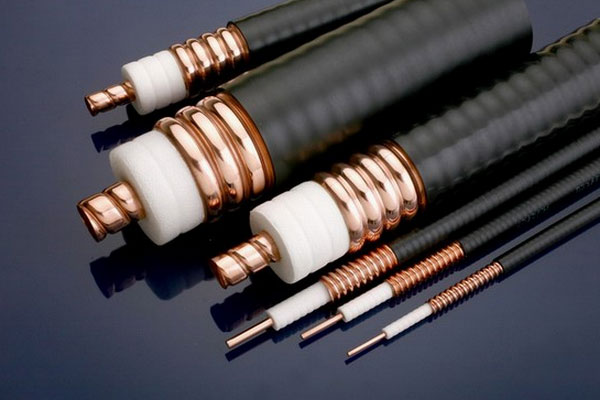
High-frequency cables play a crucial role in modern communication systems, serving as vital conduits for transmitting data at elevated frequencies. These specialized cables, designed to minimize signal loss and interference, are essential for applications such as telecommunications, broadcasting, and high-speed internet connections. Their construction typically features materials that can handle the unique demands of high-frequency signals, including low-loss dielectrics and sturdy shielding mechanisms to prevent electromagnetic interference.
One of the key characteristics of high-frequency cables is their impedance, which is usually standardized to ensure compatibility with various electronic systems. For instance, 50-ohm and 75-ohm cables are commonly used in applications ranging from radio frequency (RF) transmission to video signals. The choice of impedance impacts the efficiency of signal transmission, making it critical for engineers to select the appropriate cable for their specific needs. Additionally, factors such as cable length, connector type, and environmental conditions can greatly affect performance, requiring careful consideration during installation.
Advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of high-frequency cables that are not only more efficient but also more robust. Innovations such as low-density polyethylene (LDPE) insulation and advanced shielding designs have resulted in cables capable of operating over a wider range of frequencies while maintaining signal integrity. As the demand for faster data transfer continues to grow, particularly with the rise of 5G and IoT technologies, the importance of high-frequency cables in infrastructure and connectivity cannot be overstated. Their ability to support high-speed communication plays a pivotal role in enabling the seamless exchange of information in today’s digital age.