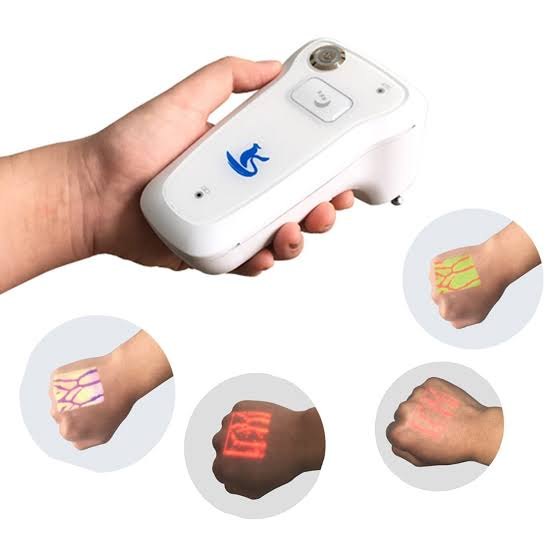
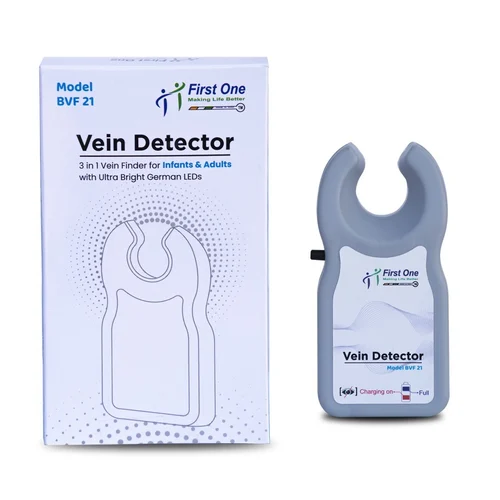
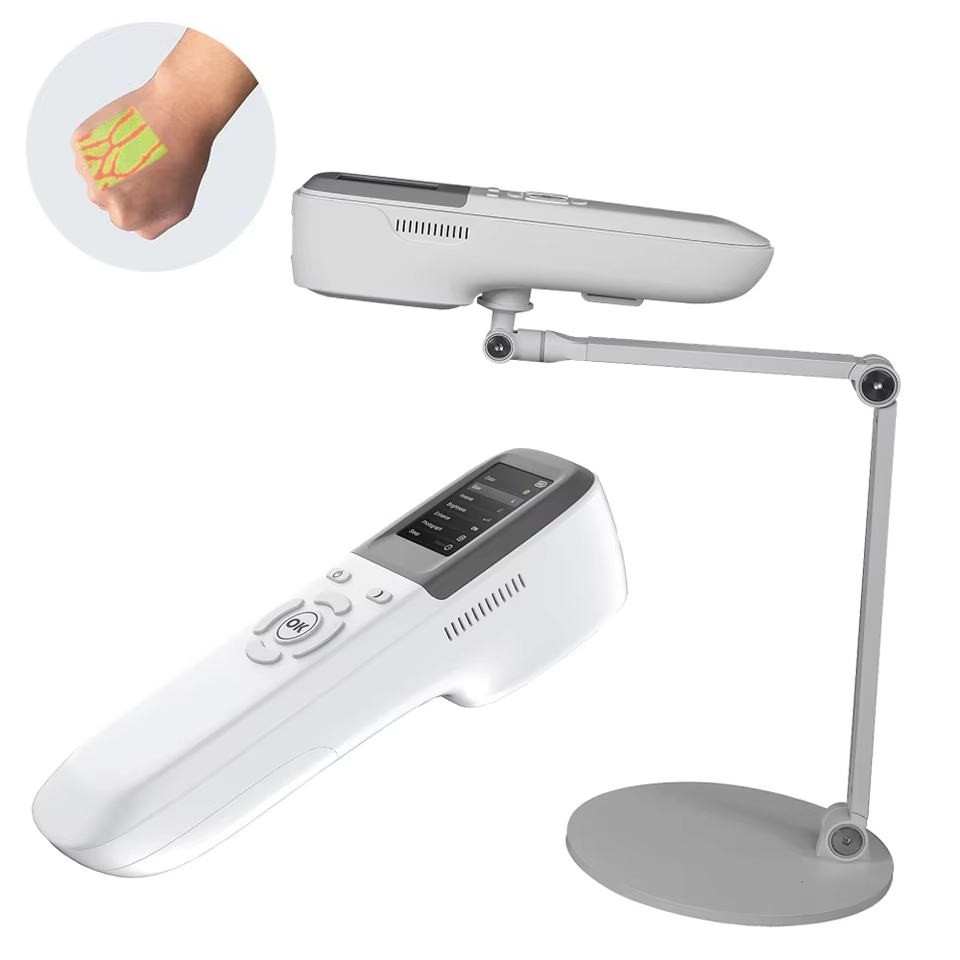
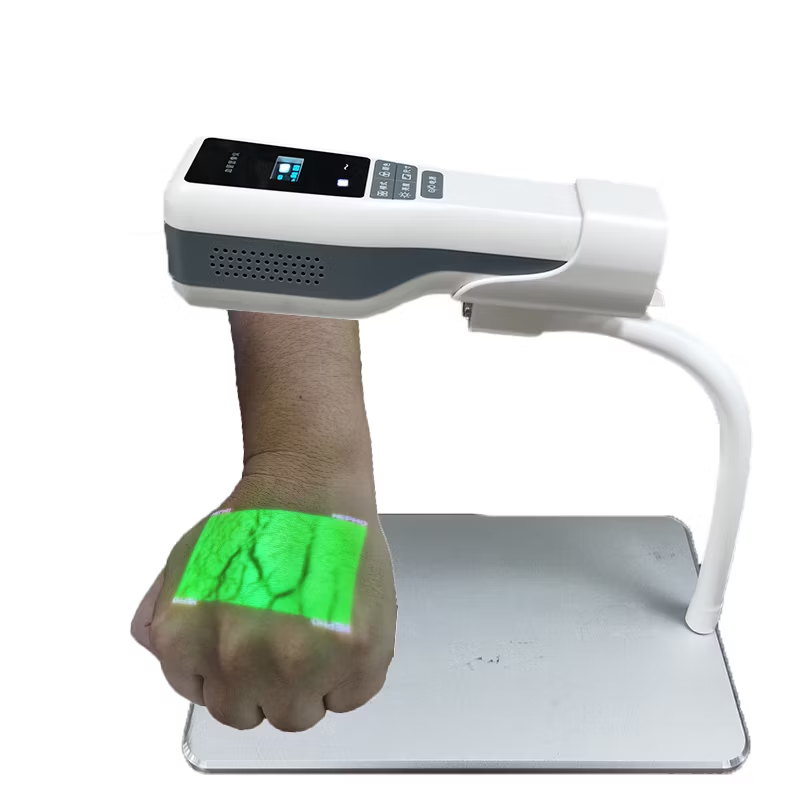
Description
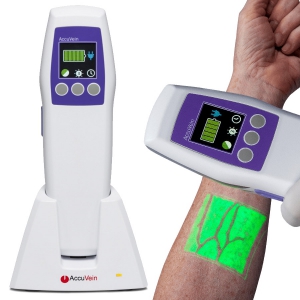
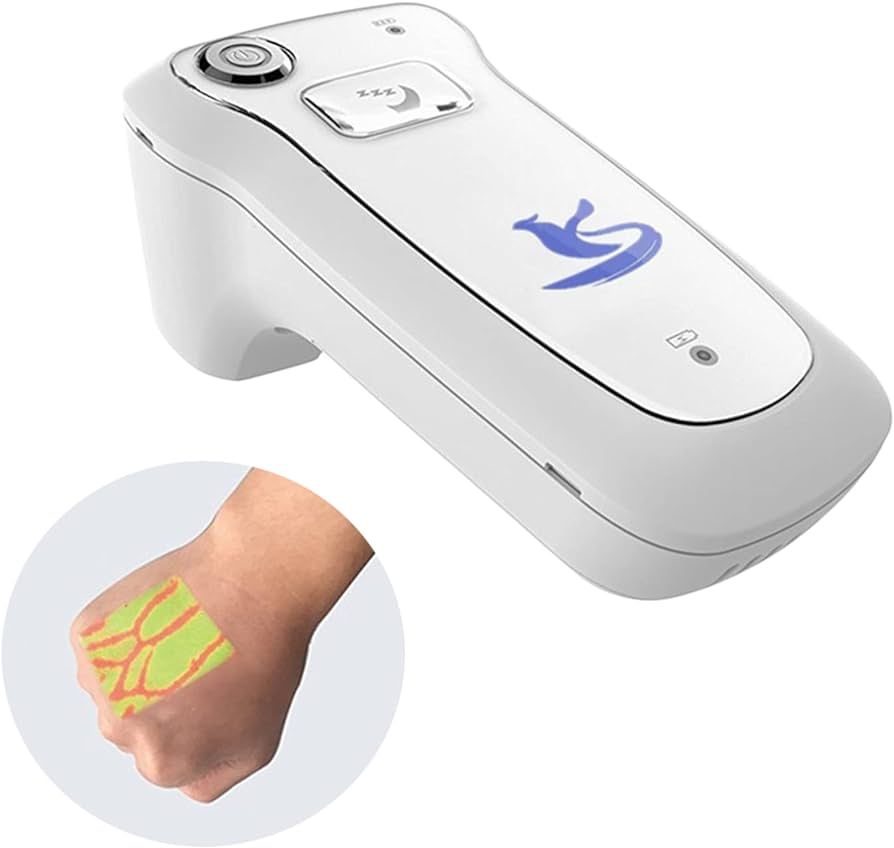
Vein visualization systems are cutting-edge medical technologies designed to enhance the visibility of veins, facilitating easier and more efficient venipuncture and other vascular procedures. These systems utilize a variety of imaging techniques, such as near-infrared light, infrared imaging, and ultrasonic waves, to create real-time maps of veins beneath the skin’s surface. This is particularly beneficial in patients with difficult venous access, such as those who are obese, elderly, or have a history of multiple venipunctures. By providing healthcare practitioners with a clear view of the vascular network, these systems significantly reduce the number of attempts needed to locate a vein, thereby minimizing patient discomfort and improving overall clinical outcomes.
In addition to improving procedural efficiency, vein visualization systems are also invaluable in pediatric care, where finding suitable veins can be challenging due to smaller size and less prominent vessels. The use of these systems facilitates a more child-friendly approach to intravenous access, ultimately fostering a more positive experience for young patients and their families. Moreover, advanced vein visualization technologies can contribute to patient safety by minimizing the risk of complications associated with misdirected or unsuccessful punctures, such as hematomas and infections.
The growing adoption of vein visualization systems in hospitals and outpatient settings highlights the ongoing advancement in medical technology. These systems not only enhance the skill set of healthcare professionals but also serve as a testament to the importance of patient-centered care. As such technologies continue to evolve, we can expect greater integration with electronic health records and telemedicine platforms, paving the way for innovative solutions that further streamline vascular access and improve patient outcomes. The future of vein visualization systems looks promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at increasing accuracy, portability, and affordability, thus making these invaluable tools accessible to a wider range of medical facilities.