Description
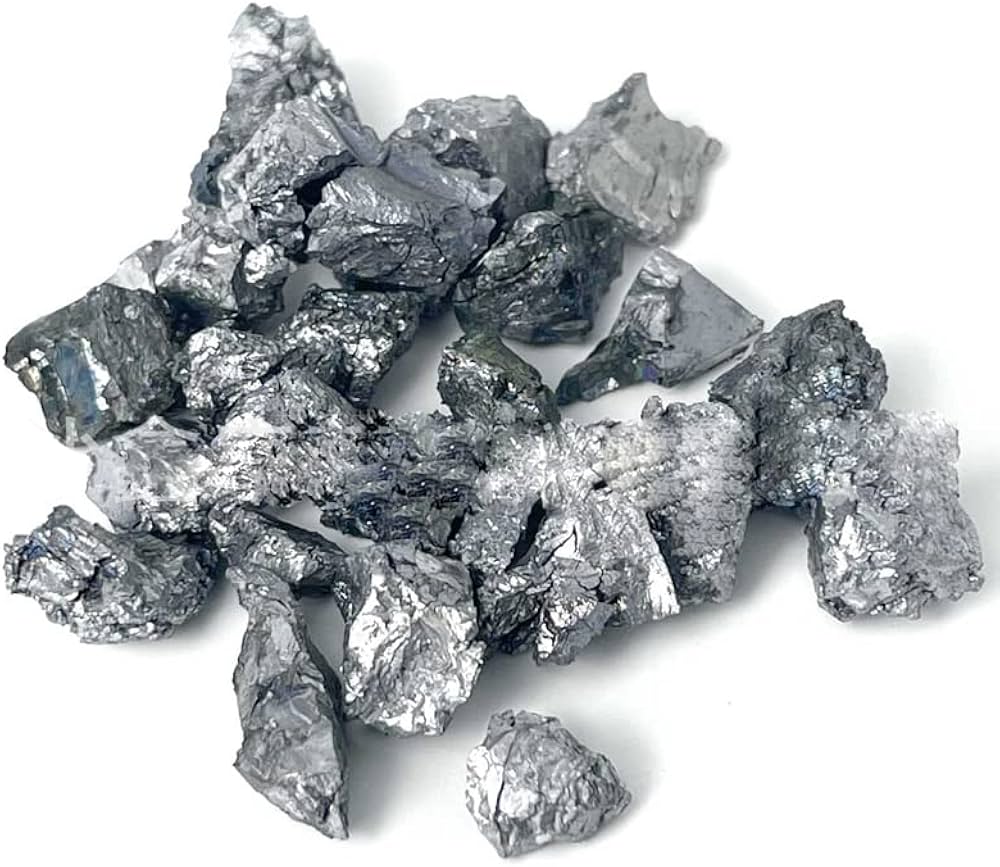
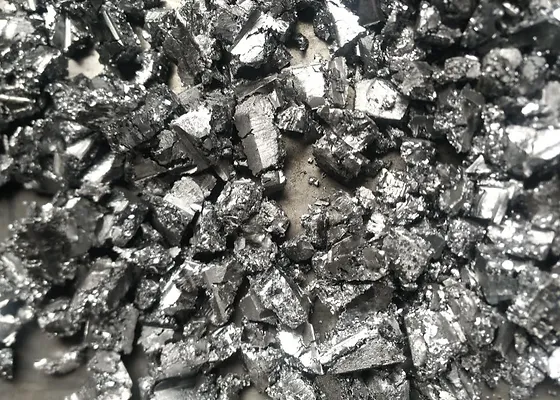
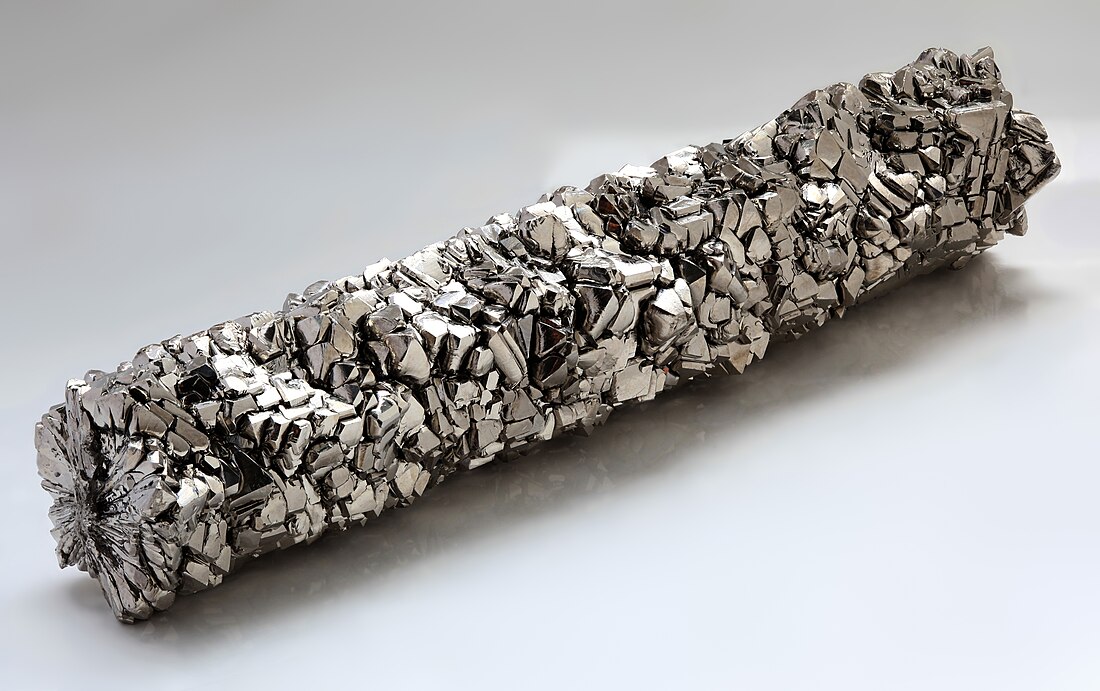
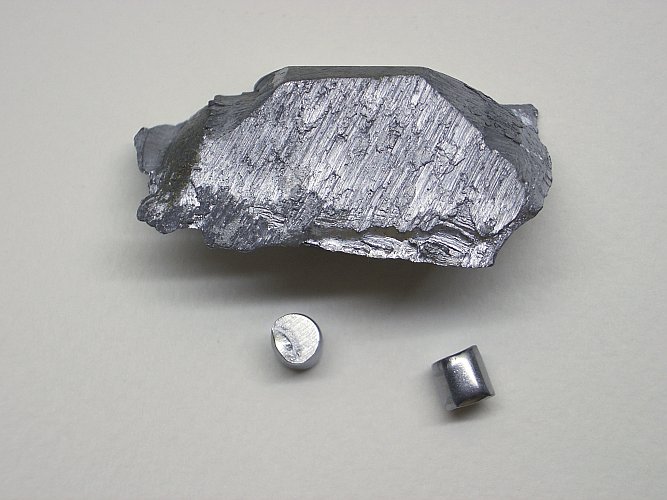
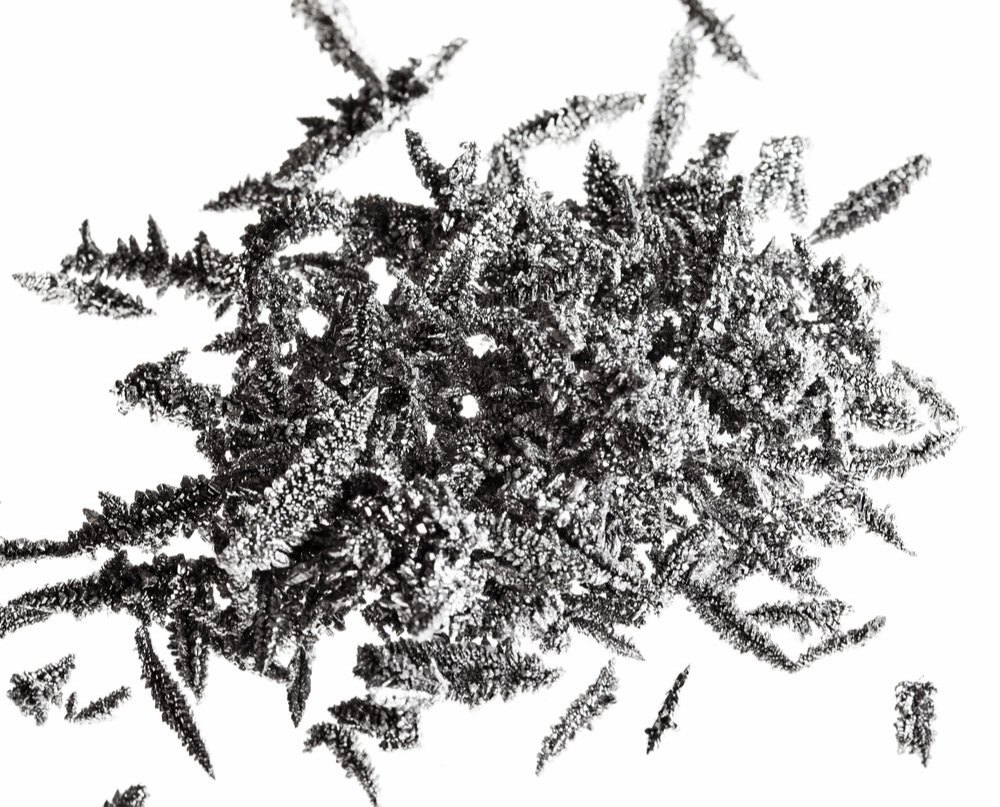
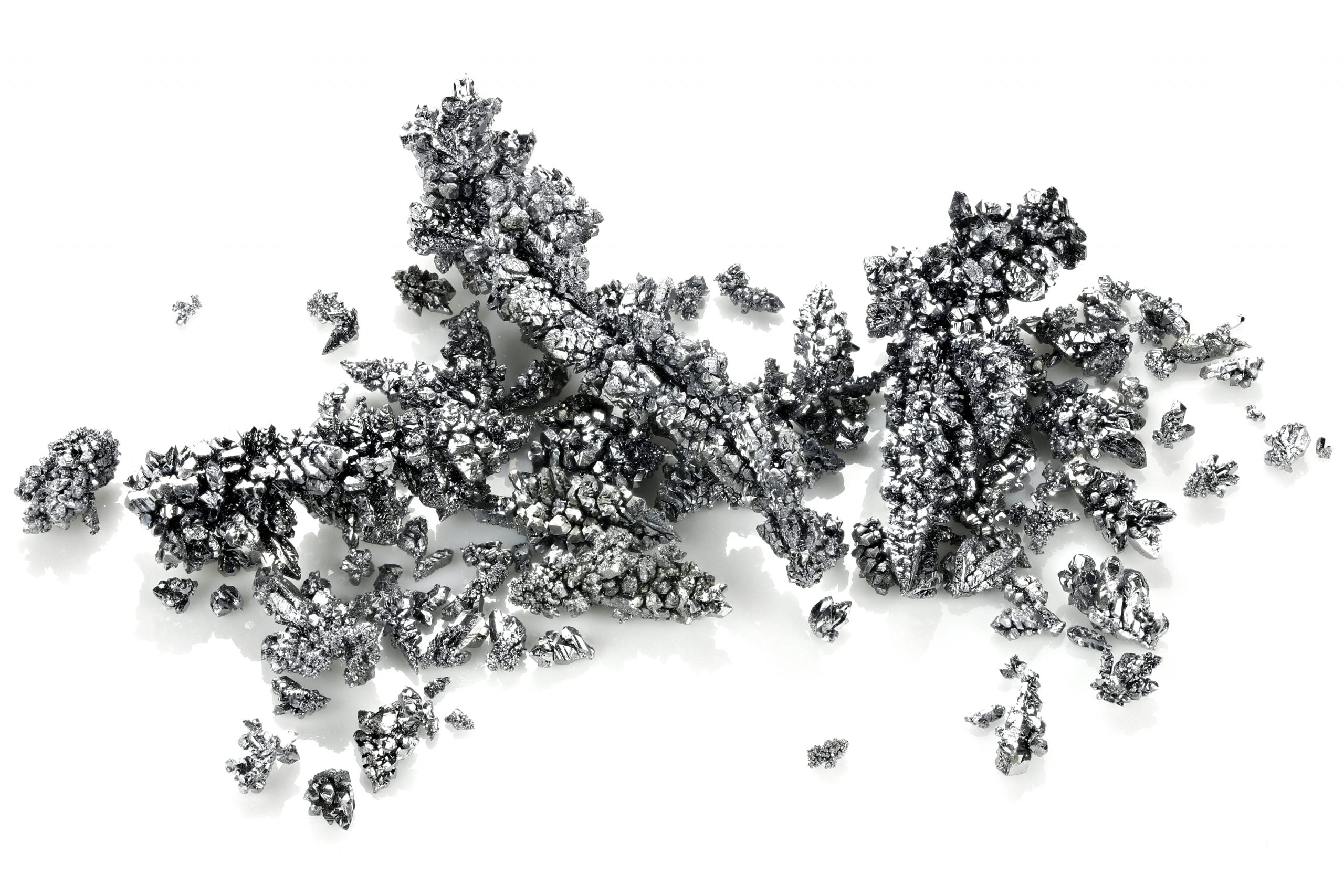
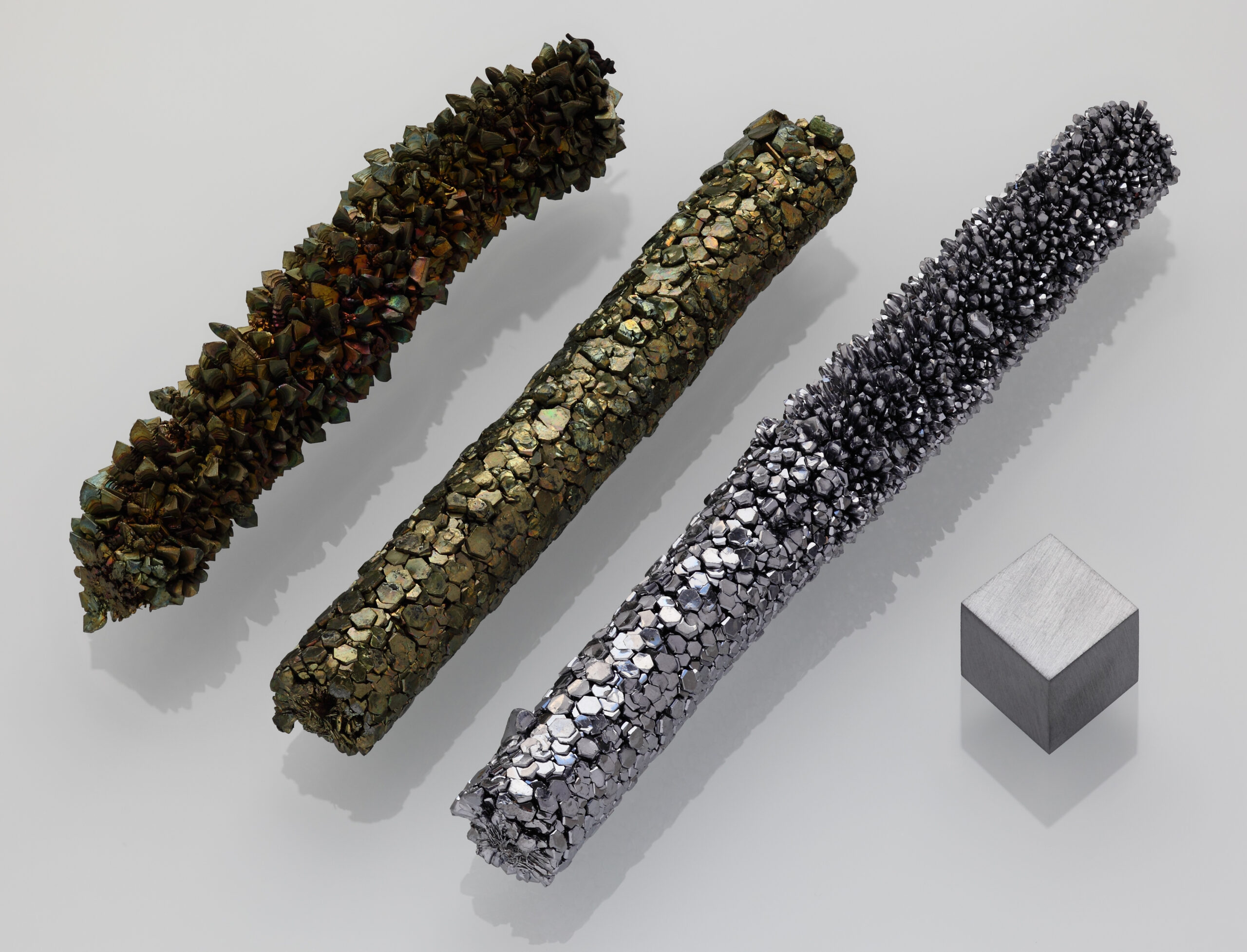
Vanadium is a versatile and essential metal that plays a significant role in various industrial applications, particularly in the production of steel and other alloys. With the chemical symbol “V” and an atomic number of 23, vanadium is typically found in nature as a part of various minerals, such as vanadinite and patronite. Its unique properties, including high strength, corrosion resistance, and excellent ability to withstand high temperatures, make it an ideal additive in metallurgical processes. In steelmaking, even small amounts of vanadium can enhance the toughness and durability of steel, making it a critical component in the construction of buildings, vehicles, and infrastructure.
In addition to its applications in metallurgy, vanadium is garnering attention within the realm of renewable energy, particularly in vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs). These batteries are known for their longevity and ability to store large amounts of energy, making them suitable for large-scale energy storage solutions. As the global push for sustainable energy sources grows, vanadium is poised to play an important role in facilitating energy transition through innovative battery technology. Furthermore, ongoing research is exploring the potential of vanadium in various fields, including catalysis and medicinal chemistry, highlighting its diverse utility and importance in modern science and industry.
Despite its beneficial uses, the extraction and processing of vanadium also raise environmental concerns. Mining activities can lead to habitat destruction, pollution, and significant energy consumption. As a result, there is a growing emphasis on responsible sourcing and the development of more sustainable practices in the vanadium supply chain. Efforts are being made to recycle vanadium from industrial materials and products to minimize waste and reduce environmental impact. As awareness of sustainable practices increases, vanadium may not only be valued for its physical properties but also for its potential contribution to a more sustainable future.