Description
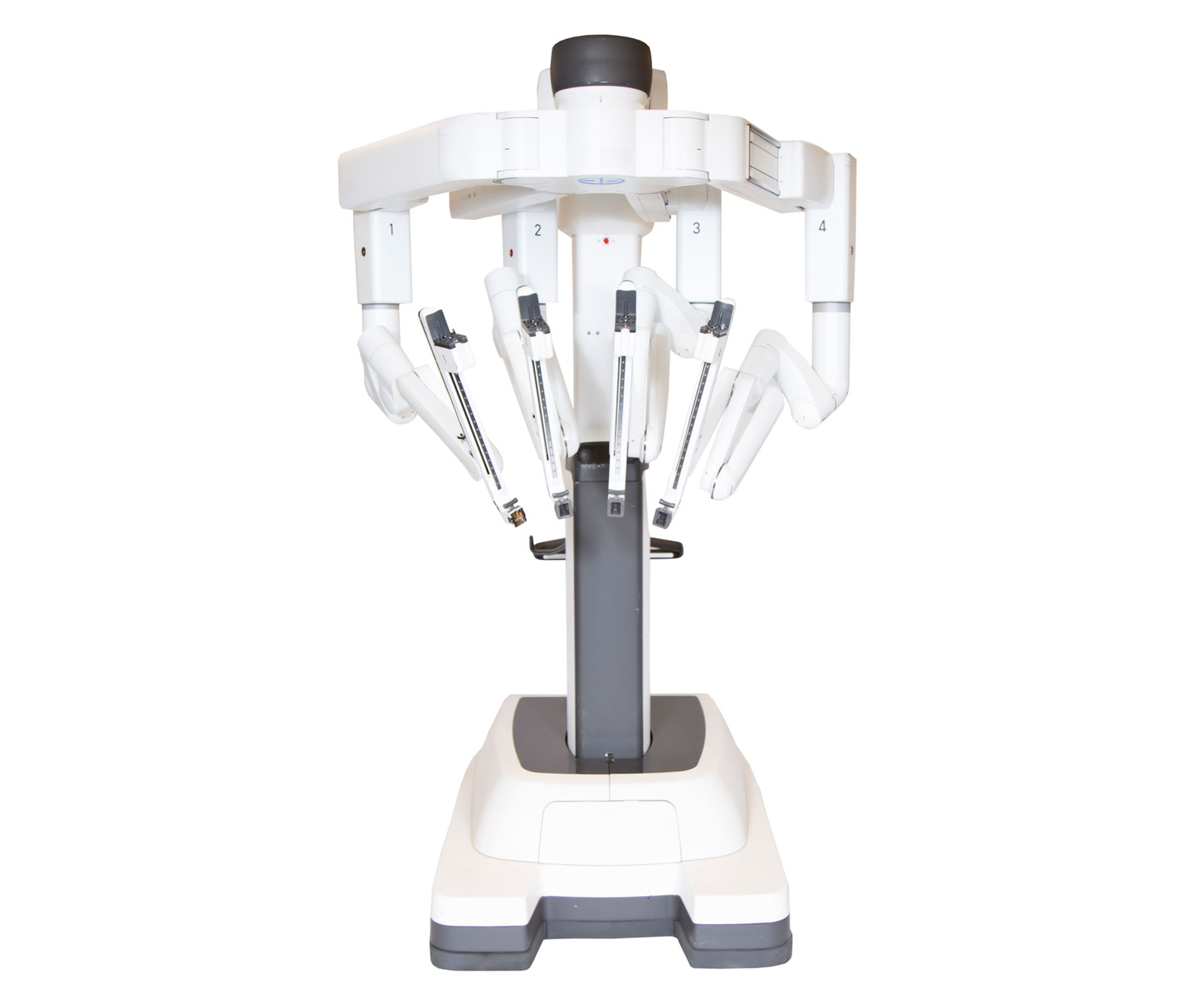
Surgical robots, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, have revolutionized the field of surgery by enhancing precision, control, and flexibility during complex procedures. Introduced in the late 1990s, the da Vinci system consists of robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments and a high-definition 3D camera, allowing surgeons to perform minimally invasive operations with unparalleled dexterity. Unlike traditional open surgery, which often requires large incisions, robotic-assisted surgery utilizes small ports, leading to reduced recovery times, less postoperative pain, and minimized scarring for patients.
The da Vinci system has been widely adopted across various surgical specialties, including urology, gynecology, and cardiothoracic surgery. Its ability to provide surgeons with a magnified view of the surgical site and the capacity to manipulate instruments in tight spaces has made it particularly invaluable for procedures such as prostatectomies and hysterectomies. Additionally, the robotic arms can replicate the natural motion of the surgeon’s hands with great precision, which is critical for delicate maneuvers, ensuring that the highest standards of safety and efficacy are maintained during surgery.
Despite the numerous advantages, the implementation of surgical robots is not without challenges. The high costs associated with purchasing and maintaining these systems can be a barrier for many healthcare facilities, potentially limiting access for patients in underserved areas. Furthermore, as with any technological advancement, there is a learning curve for surgeons in mastering robotic techniques. Ongoing training and experience are essential to harnessing the full potential of robotic surgery, which emphasizes the importance of continuing education in the medical field.
In conclusion, surgical robots like the da Vinci Surgical System represent a significant advancement in surgical technology, offering numerous benefits for both patients and surgeons alike. As the technology continues to evolve, it promises to further enhance surgical outcomes and expand the possibilities of minimally invasive procedures, ultimately improving the quality of care in the healthcare system.