Description
EHV XLPE (Extra High Voltage Cross-Linked Polyethylene) power cables are a cornerstone of modern electricity transmission, enabling the efficient and reliable transport of large amounts of power over long distances. These cables are designed to operate at voltages exceeding 230 kV, making them critical components of national and regional power grids.
The use of XLPE insulation offers significant advantages over traditional oil-filled or paper-insulated cables, including superior electrical properties, higher operating temperatures, reduced dielectric losses, and simplified maintenance requirements. This translates to lower overall system costs and enhanced grid stability.
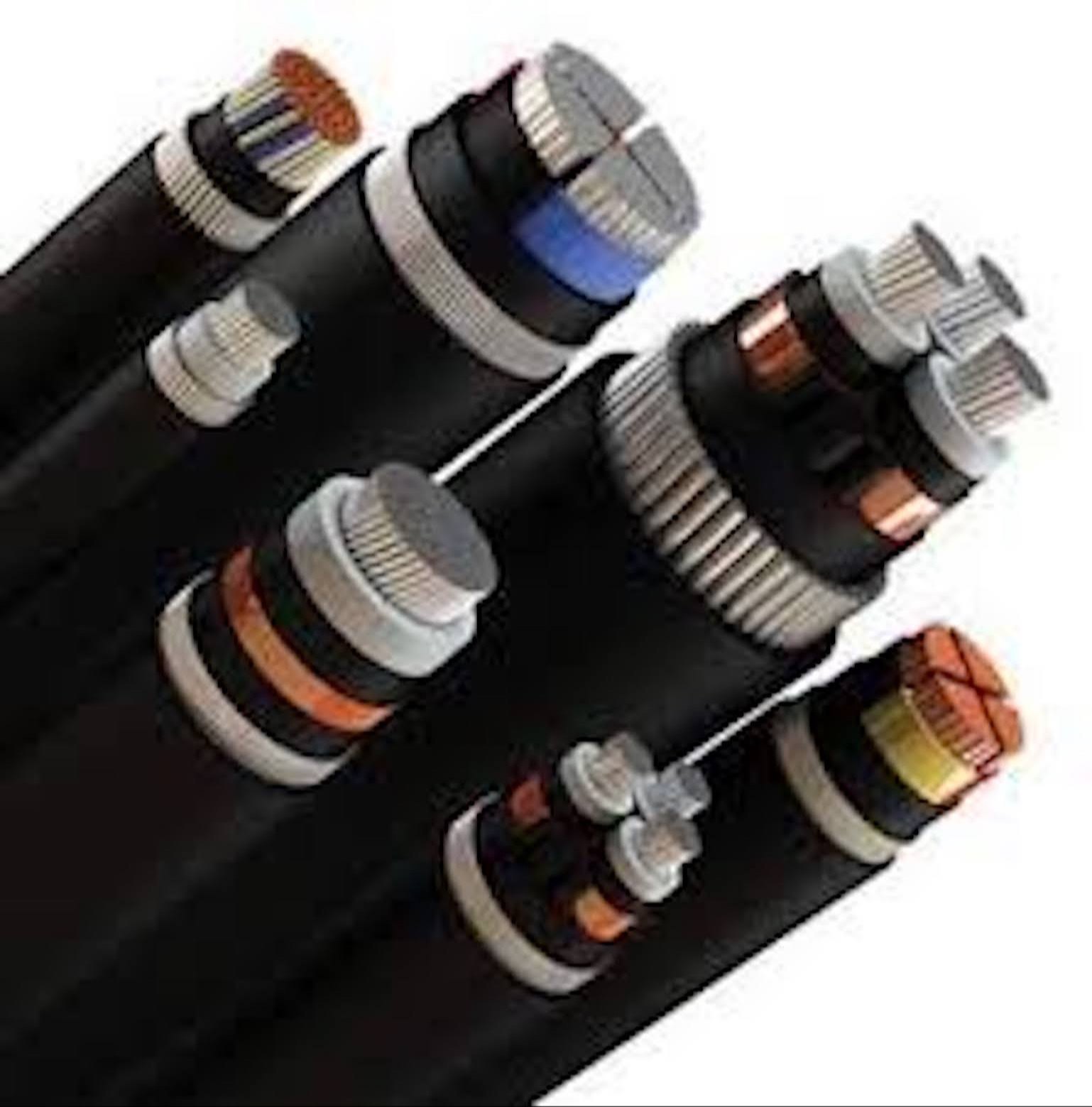
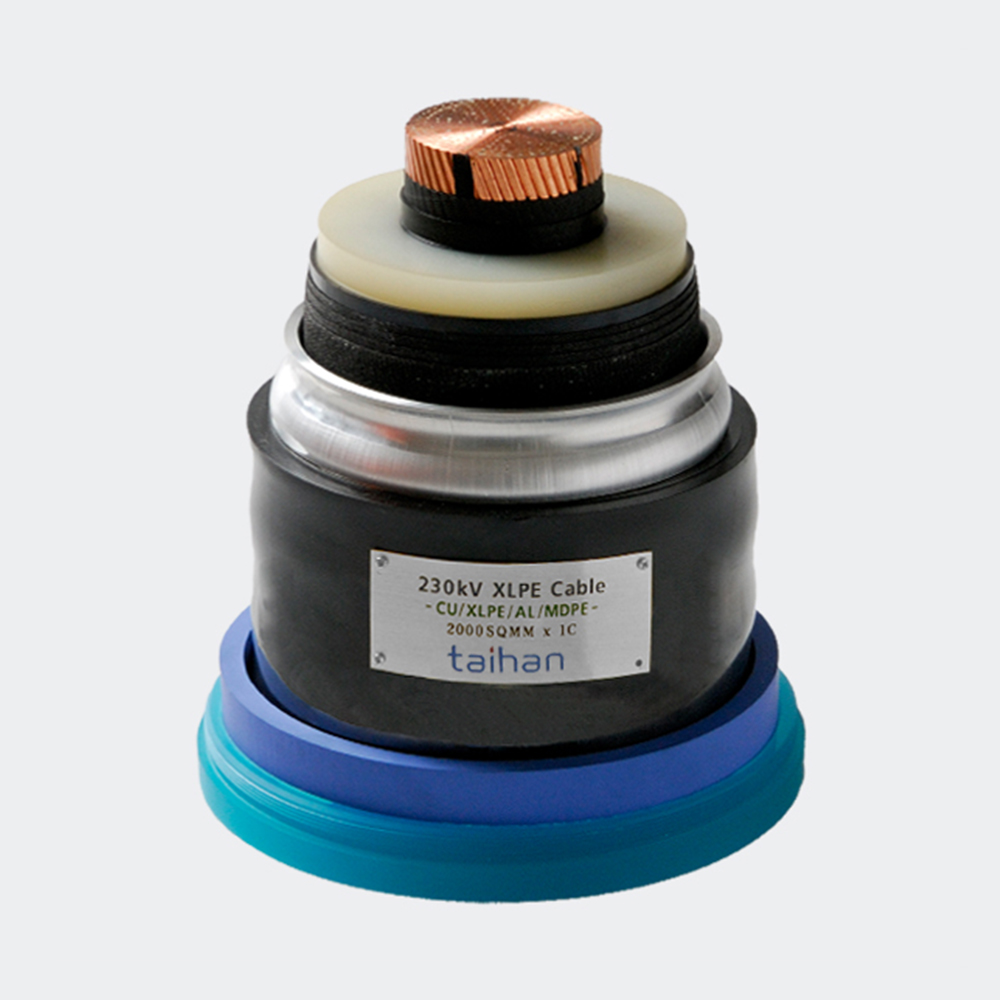
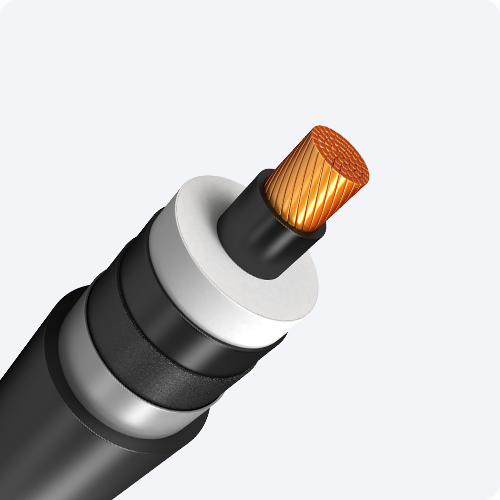
The construction of an EHV XLPE cable is a complex process involving multiple layers, each serving a specific function. Starting from the conductor, typically made of copper or aluminum, several semiconducting layers are extruded over the conductor to provide a smooth electrical field distribution and prevent partial discharge.
The XLPE insulation layer is then applied, its quality and thickness being paramount to the cable’s performance and longevity. An outer semiconducting layer, metallic screen, and an outer sheath, usually made of polyethylene (PE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), complete the cable assembly, providing mechanical protection and corrosion resistance.
The manufacturing of EHV XLPE cables requires sophisticated equipment and stringent quality control measures. The cross-linking process, which transforms the thermoplastic polyethylene into a thermoset material, is crucial for achieving the desired electrical and mechanical properties.
Degassing and testing are also vital to ensure the cable meets the rigorous standards required for EHV applications. With increasing demands for renewable energy integration and grid modernization, EHV XLPE cables are playing an increasingly important role in delivering power reliably and efficiently to meet the needs of a growing global population.