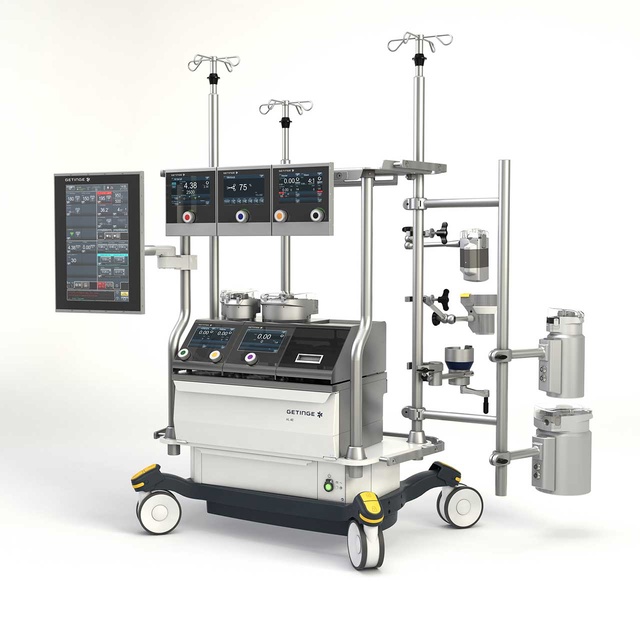
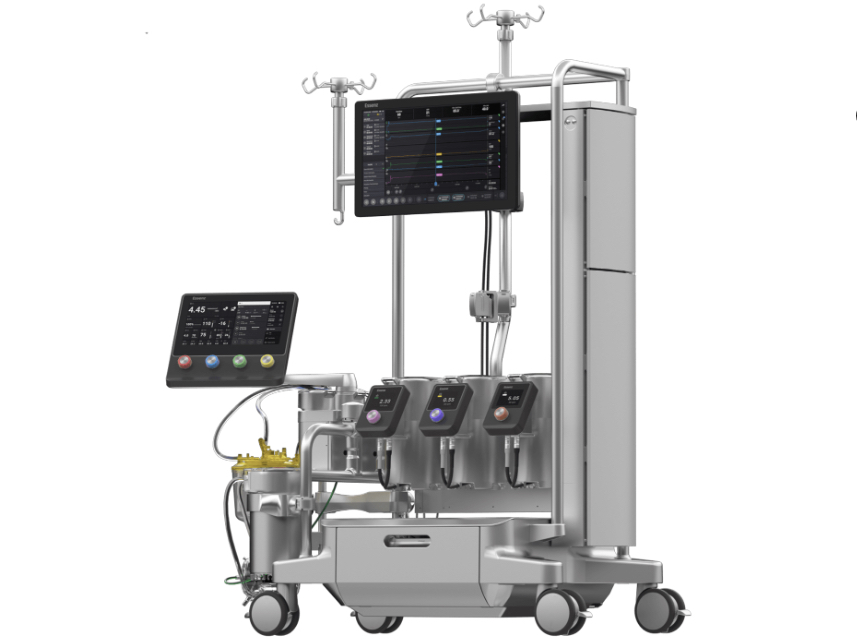
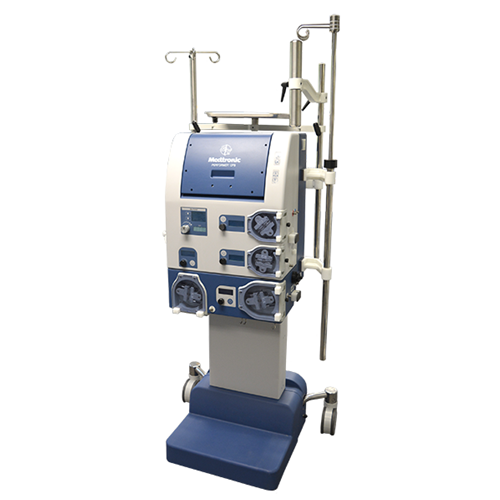
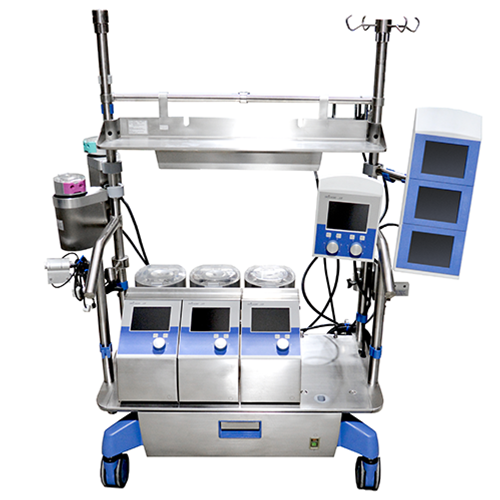
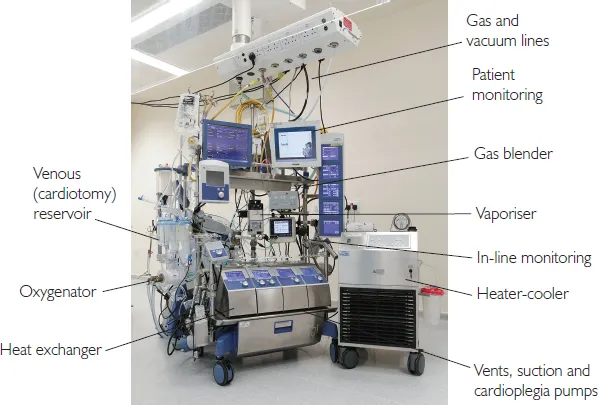
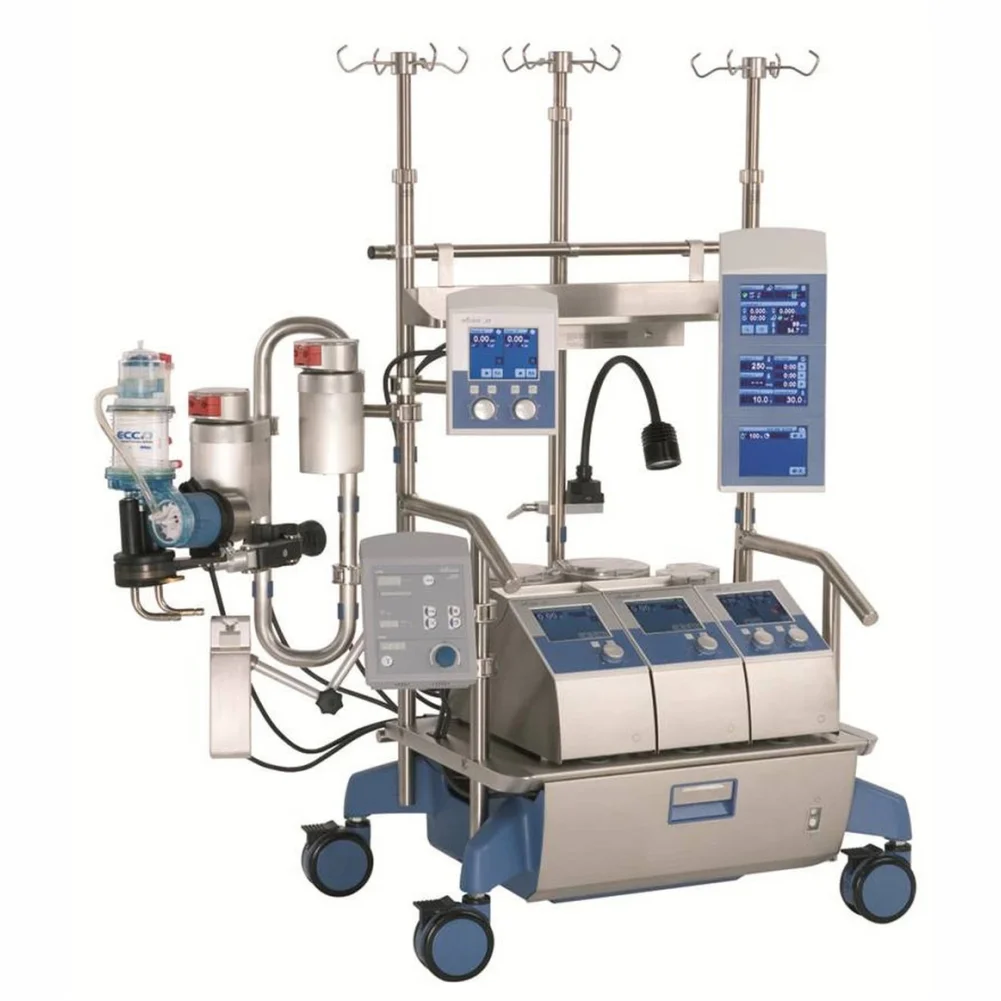
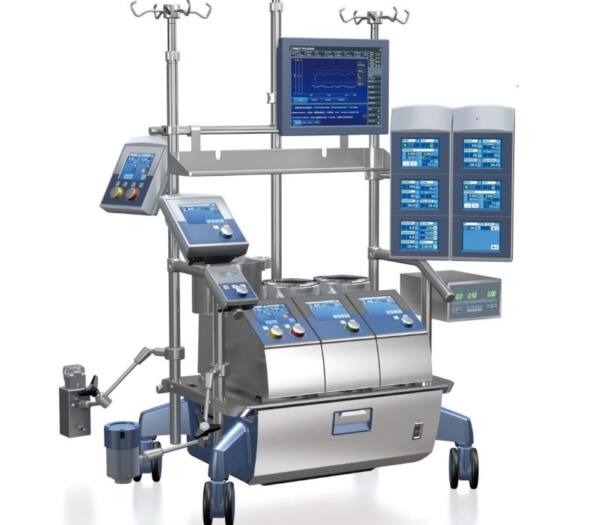
Description
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) machines play a critical role in modern cardiac surgery, facilitating complex procedures by taking over the functions of the heart and lungs. During surgeries such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or heart valve repairs, the CPB machine allows surgeons to operate on a still and bloodless heart. By diverting blood away from the heart and lungs, the machine oxygenates the blood and removes carbon dioxide, effectively mimicking the functions of these vital organs. This system is essential for maintaining adequate blood flow and oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues while the heart is temporarily stopped.
The technology behind CPB machines has advanced significantly over the years, incorporating features that enhance their safety and efficiency. Modern machines are equipped with sophisticated monitoring systems that provide real-time data on blood flow, oxygen levels, and other critical parameters. Additionally, innovations such as miniaturized components and biocompatible materials have improved patient outcomes by reducing complications associated with the bypass process. The use of heat exchangers, for example, enables precise temperature control, which can be crucial for protecting the brain and other organs during surgery, particularly in cases involving prolonged periods of bypass.
Despite their benefits, the use of cardiopulmonary bypass is not without risks. Patients may experience complications such as bleeding, infection, and inflammatory responses due to the interaction between blood and the artificial surfaces of the CPB circuit. Understanding these risks has prompted ongoing research into optimizing CPB techniques and materials to minimize adverse effects. Additionally, advances in less invasive surgical approaches and the development of alternative perfusion methods continue to evolve, potentially reshaping the landscape of cardiac surgery.
In summary, cardiopulmonary bypass machines are an indispensable tool in the field of cardiac surgery, allowing for complex interventions with enhanced safety and efficacy. While challenges remain, ongoing innovations and research are focused on maximizing patient outcomes and minimizing complications associated with CPB. As surgical techniques continue to advance, the role of these machines may evolve, reflecting the ever-changing dynamics of cardiac care.