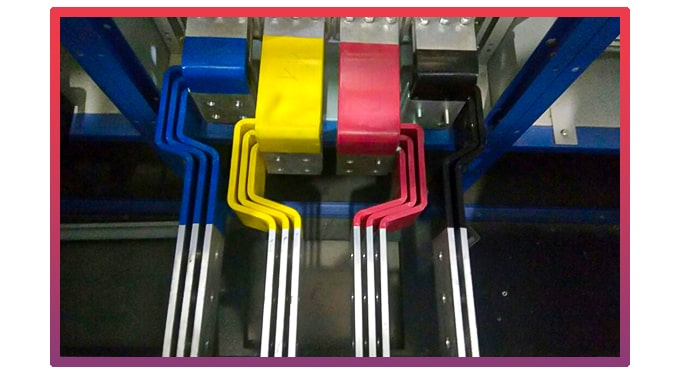
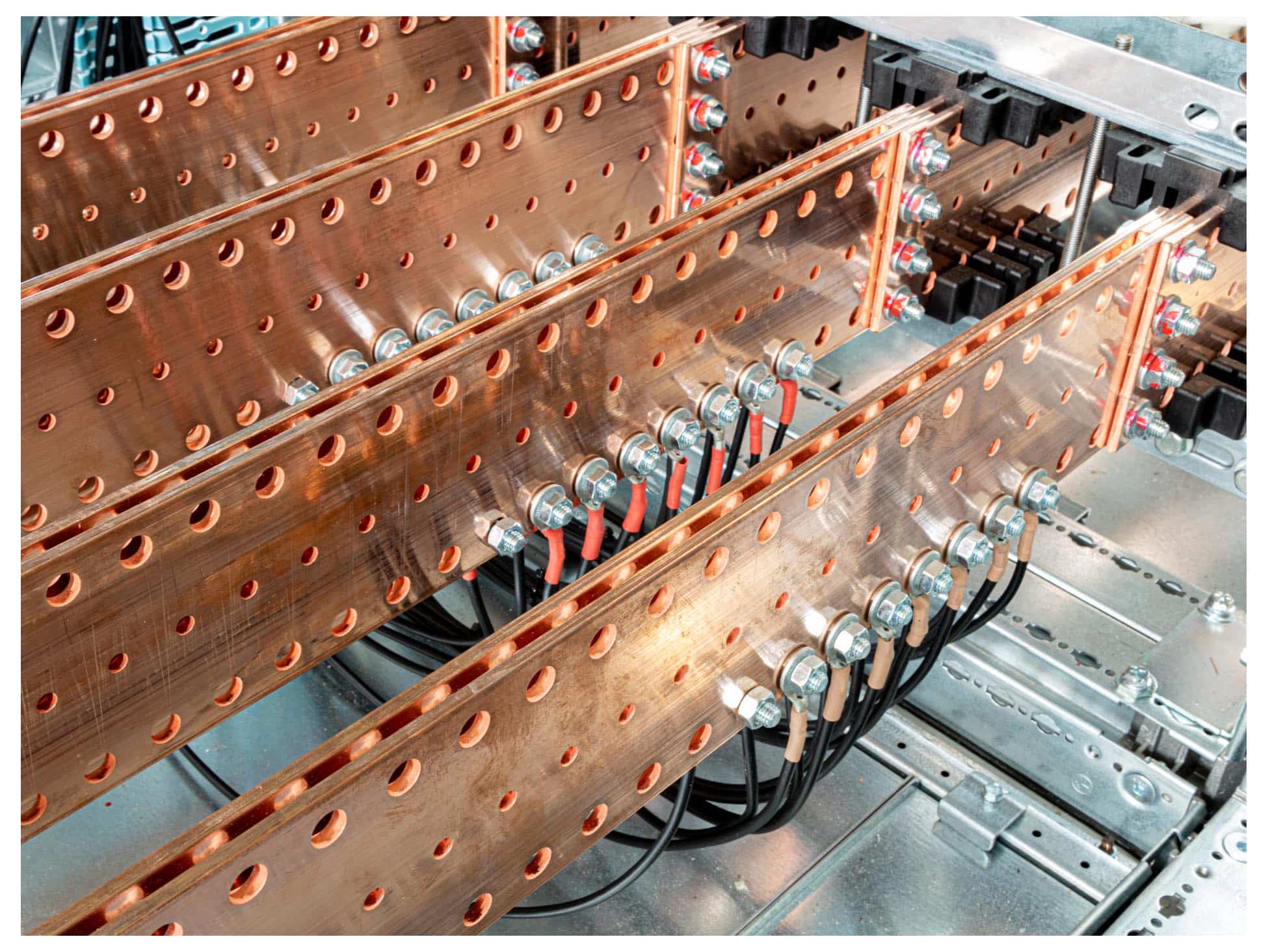
Description
Different coating materials provide different conductivity limits and variations in the length of a product’s useful life. Busbars can also come in a multitude of shapes and sizes which affect the ampacity of the product. The word ampacity refers to the maximum amount of electric current a conductor can carry before sustaining critical levels of deterioration.
Busbars can either be fully enclosed or designed with a continuous access open-channel. Fully enclosed busbars provide similar benefits of reduced installation time and increased performance while supporting higher ampacities.
Other reasons that busbars are popular:
Reduced facility costs because less construction labor means installation is less expensive and there are no costly changes and outside labor costs for electrical specialists.
Faster installation because building projects are up and running faster plus the ability to add, remove or relocate power easily and quickly with no downtime.
Flexibility for the future because some plug-in units can be disconnected and reconnected without de-energizing, require no routine maintenance and are faster and less costly for expansion or remodeling.
Environmentally friendly because busbars often require fewer installation materials and plug-in outlets are reusable and re-locatable.
Recent advancements to the structural integrity of busbar systems have proven changing the shape of the copper busbar greatly improves the efficiency, exposing more of the copper surface area and increasing a balanced electrical flow while decreasing its ampacity.
Where are busbars used?
Busbar systems are used to safely implement three-phase power distribution systems, often in large environments. Busbars are found in
- Factories
- Data centers
- Retail facilities
- Laboratories
- Hospitals
- Universities
- Technology settings
Busbars range greatly in size and the size is dependent on the use. Common commercial and industrial busbars sizes are:
40, 50, 60, 100/160, 225, 250, 400, 600/630, 800, 1000, and 1200/1250 amps
They can also be used as housing for expandable track lighting which runs from one single power supply.
For applications in which higher ampacity is required, high power busbar trunking systems can provide up to 6300 amps. Common high power busbar amperages include:
630, 800, 1000, 1250, 1600, 2000, 2500, 3200, 4000, 5000, and 6300 amps
What is a copper busbar?
Copper is a common conductive metal used in busbars and many electrical utilities around the world. Copper is chosen for it’s resilience to higher temperatures, providing extra security during short circuit situations.
Other benefits provided by the use of copper are:
- High conductivity
- Resistance to damage
- Higher performance in clamped joints
- Lower coefficient of linear expansion
- Long lifespan
- High recovery value
- Higher modulus of elasticity
- The surface of copper naturally oxidizes forming a thin hard layer on the surface which remains conductive. Exposed aluminum surfaces also form an oxidized film. However, this film is not conductive and leads to long term reliability issues with joints.
For an (extremely) in-depth technical analysis on the applications and conductivity levels of copper busbars, visit this study by the Copper Alliance Association.
Why are U-shaped busbars popular?
U-shaped busbar systems deliver continuous and reliable connections to power while maximizing the potential tappable locations. The U-shape supports even weight distribution; mitigating any distortion resulting from excessive force.
This system enables simple expansion, reconfiguration, or relocation operations and the shape applies continuous pressure to every joint creating a solid connection and eliminating the need for routine maintenance.