Description
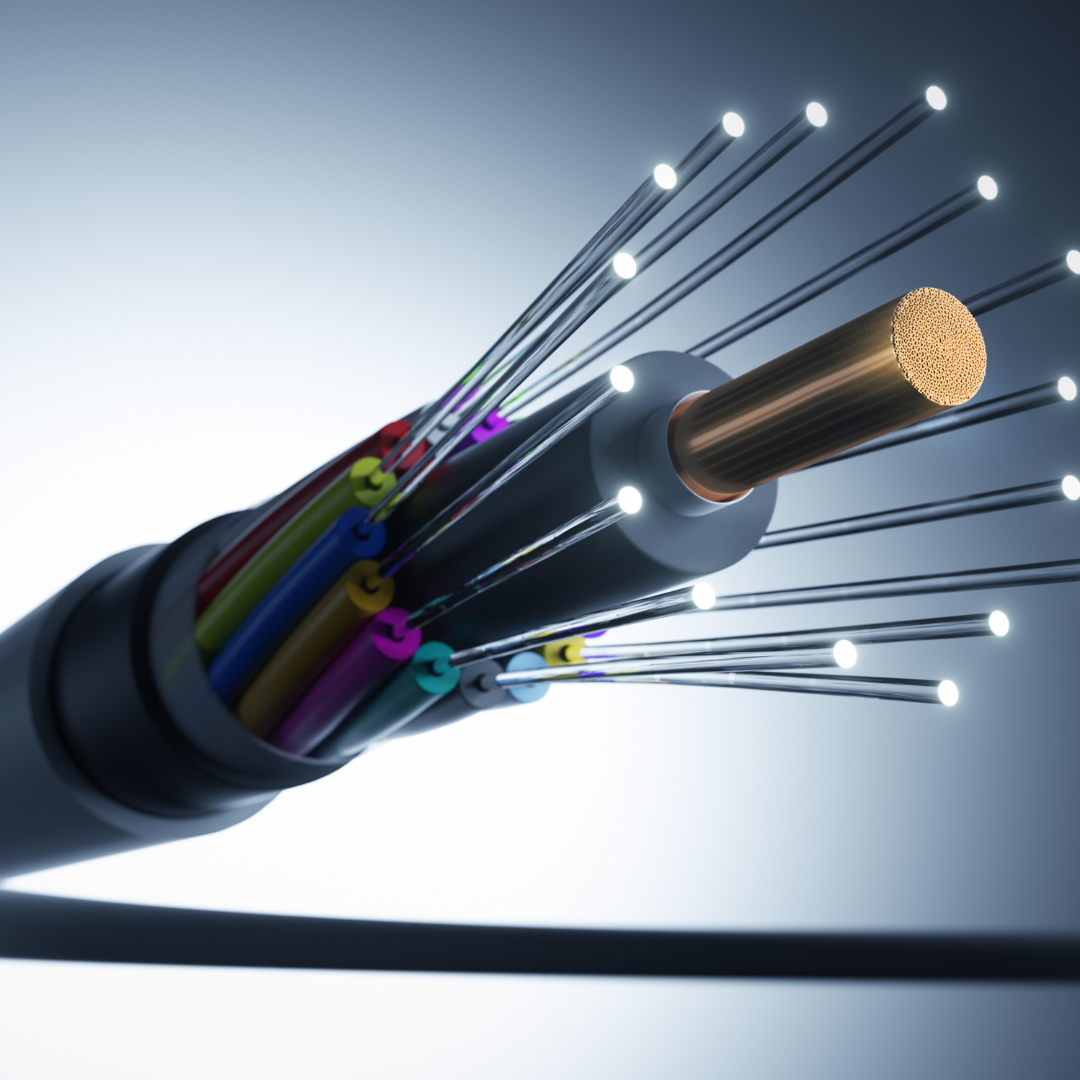
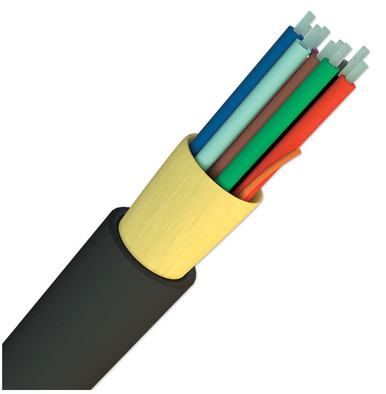
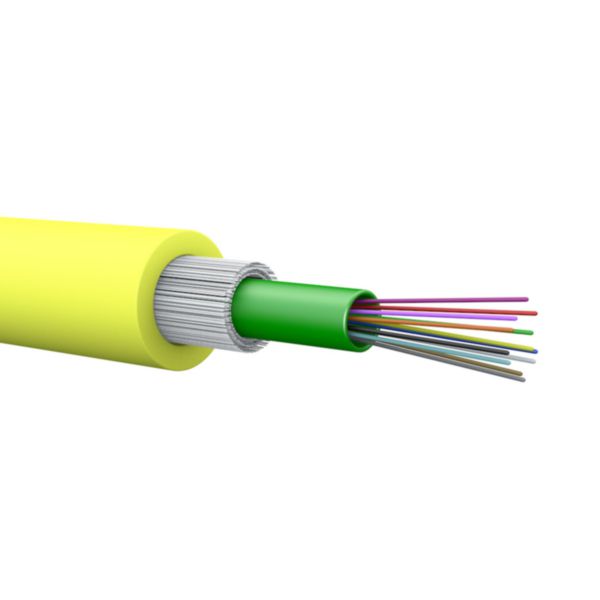
Fiber optic cables are a cornerstone of modern telecommunications and networking, delivering high-speed data transmission with remarkable efficiency. Unlike traditional copper cables, which transmit data as electrical signals, fiber optic cables use light pulses to carry information. This fundamental difference allows for significantly higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances without degradation of signal quality. As a result, fiber optics are increasingly utilized in various applications, from internet infrastructure to medical devices, where rapid data transfer is crucial.
One of the key advantages of fiber optic cables is their resistance to interference and electromagnetic noise. Since the data is transmitted via light rather than electrical signals, fiber optics are less susceptible to disruptions caused by external electronic interference. This feature makes them ideal for environments where high reliability and performance are essential, such as in hospitals, data centers, and industrial settings. Additionally, fiber optic cables are lightweight and can be installed in flexible configurations, making them an appealing option for both urban and rural network expansions.
Furthermore, the growing demand for faster internet and data services has spurred a rapid expansion of fiber optic infrastructure worldwide. Many telecommunications companies are investing heavily in the deployment of fiber networks to meet consumer expectations for higher speeds and greater reliability. As technologies such as 5G evolve and the Internet of Things (IoT) becomes more prevalent, fiber optics will play an indispensable role in enabling seamless connectivity and communication across devices and platforms. As innovation continues, the future of fiber optic technology looks promising, with advancements in materials and design poised to enhance performance even further.