Description
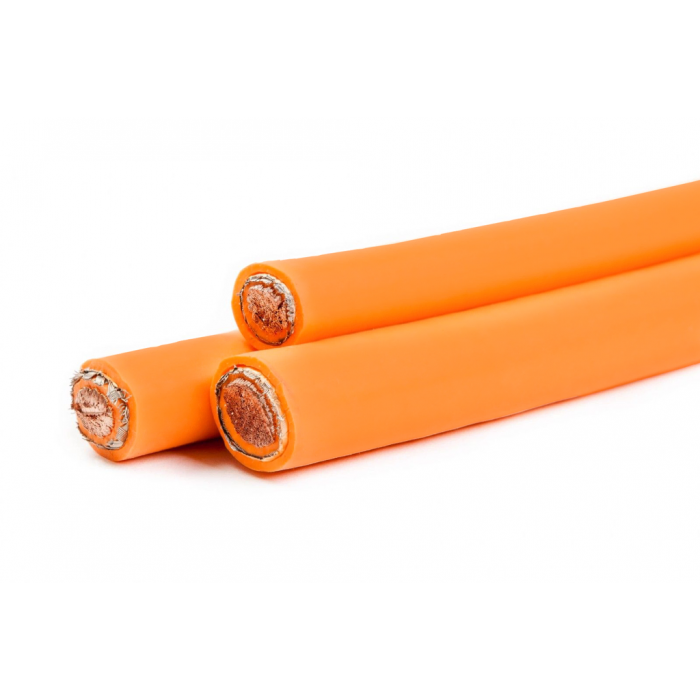
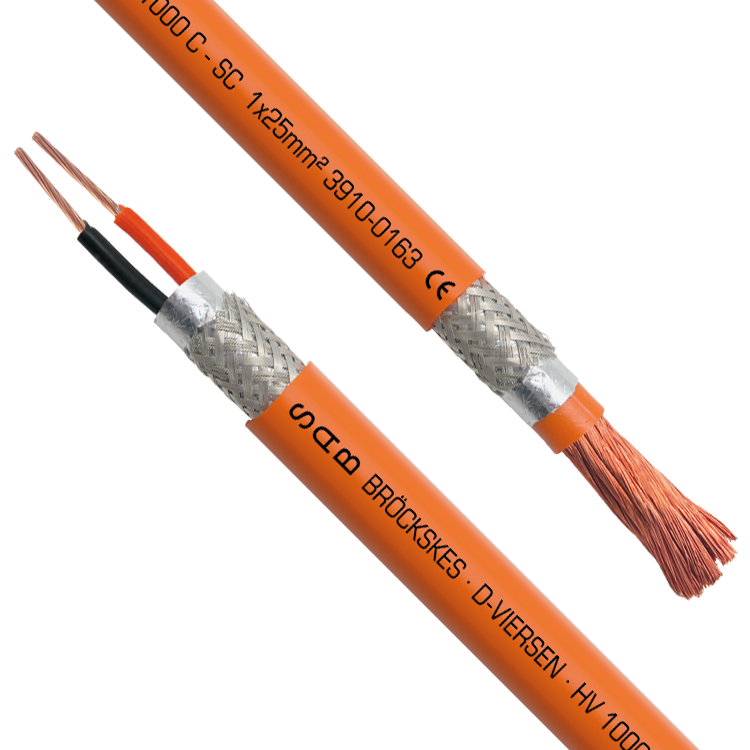
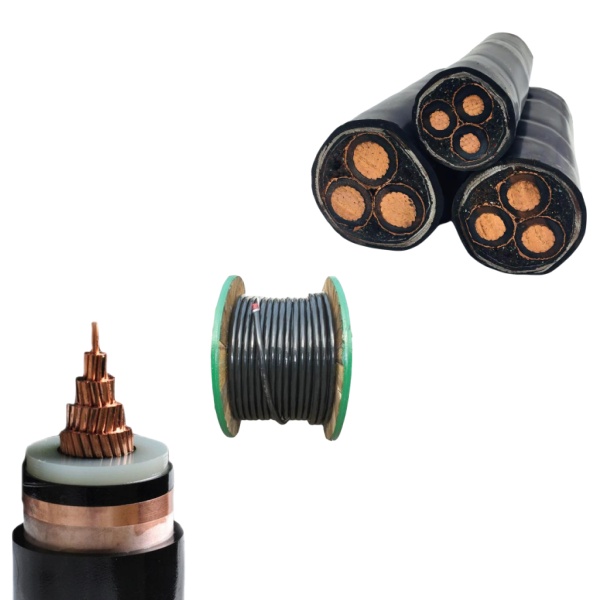
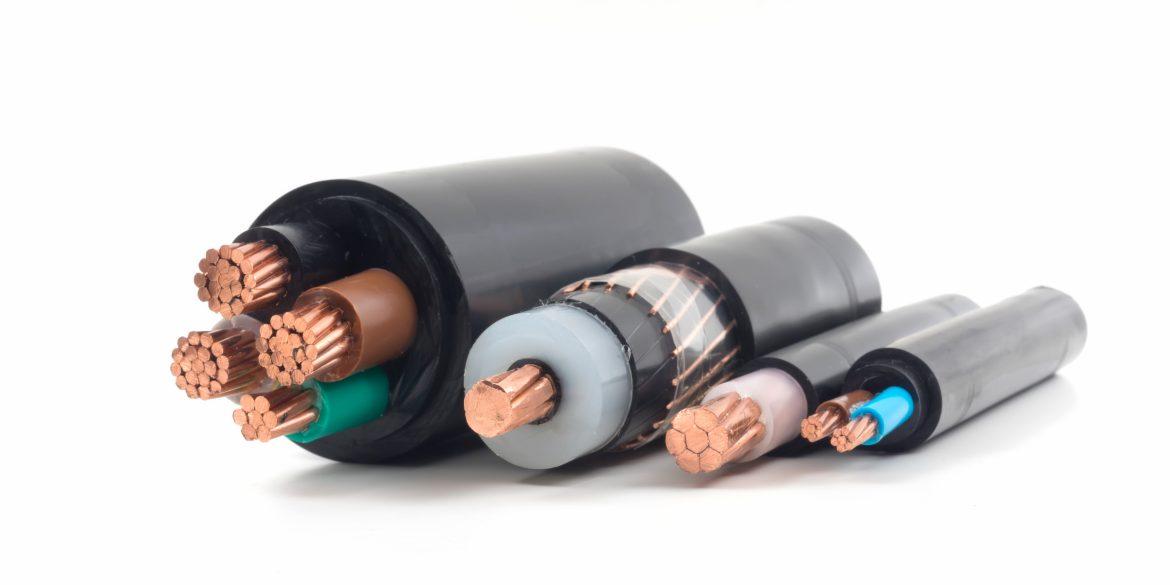
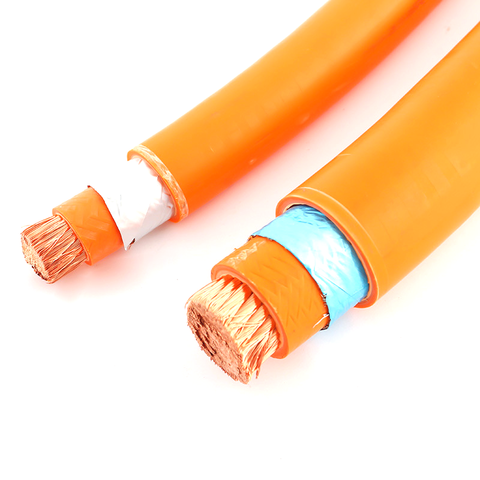
High Voltage (HV) power cables are critical components in the electrical power distribution and transmission sectors, designed to carry large amounts of electrical energy over long distances while minimizing losses. These cables typically operate at voltages exceeding 1 kV, with some applications reaching several hundred kilovolts (kV). Due to the nature of high voltage transmission, these cables must be constructed with robust insulation materials that can withstand not only the electrical stress but also environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, and mechanical impacts. Common insulating materials include cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) and ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), both valued for their excellent dielectric properties and durability.
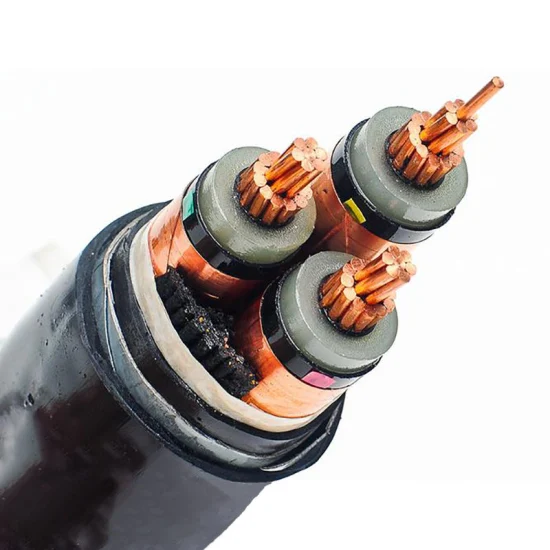
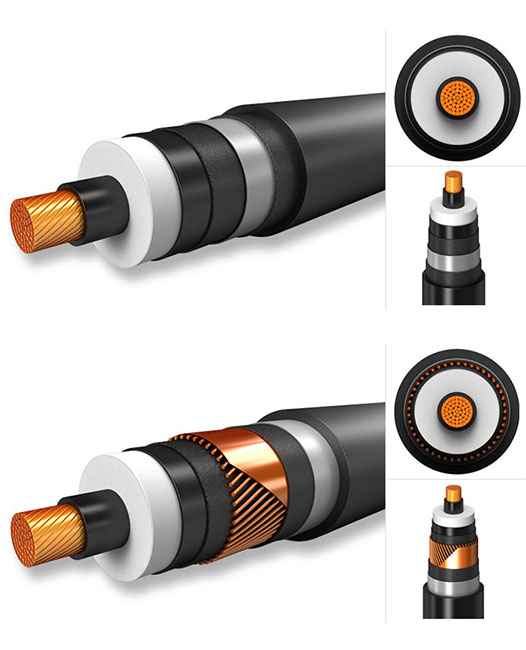
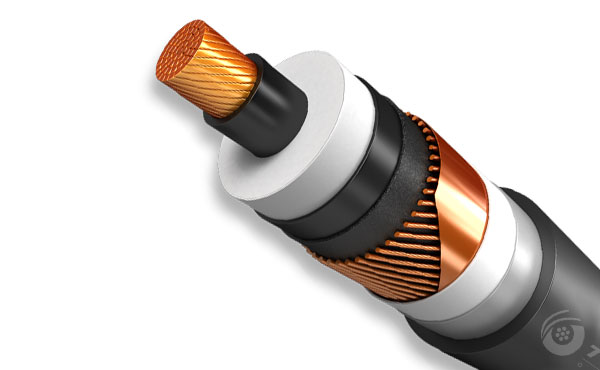
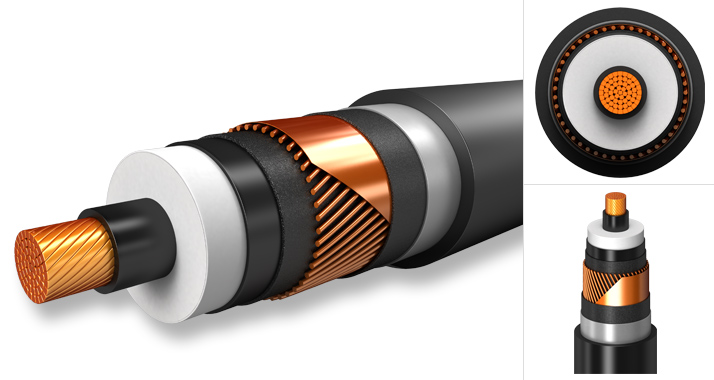
The design and use of HV power cables are guided by international standards to ensure safety and efficiency. These cables often feature a complex multi-layer construction, consisting of conductors, insulating layers, shielding, and protective coverings. The conductor materials, typically copper or aluminum, play a vital role in determining the cable’s conductivity and overall performance. Shielding is also crucial, as it helps to prevent electromagnetic interference and ensures that the electric field does not extend beyond the cable, thereby reducing the risk of electrical hazards.
In addition to their technical specifications, the deployment of HV power cables is central to modern energy infrastructure, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, into the grid. As cities grow and the demand for electricity increases, the efficient transmission of power from generation sites to consumption centers becomes paramount. This leads to ongoing advancements in cable technology, including innovations aimed at enhancing thermal performance, increasing transmission capacity, and improving environmental sustainability. As such, HV power cables not only support the current energy framework but also pave the way for future developments in clean energy and smart grid systems, promoting a more sustainable and reliable power supply.