Description
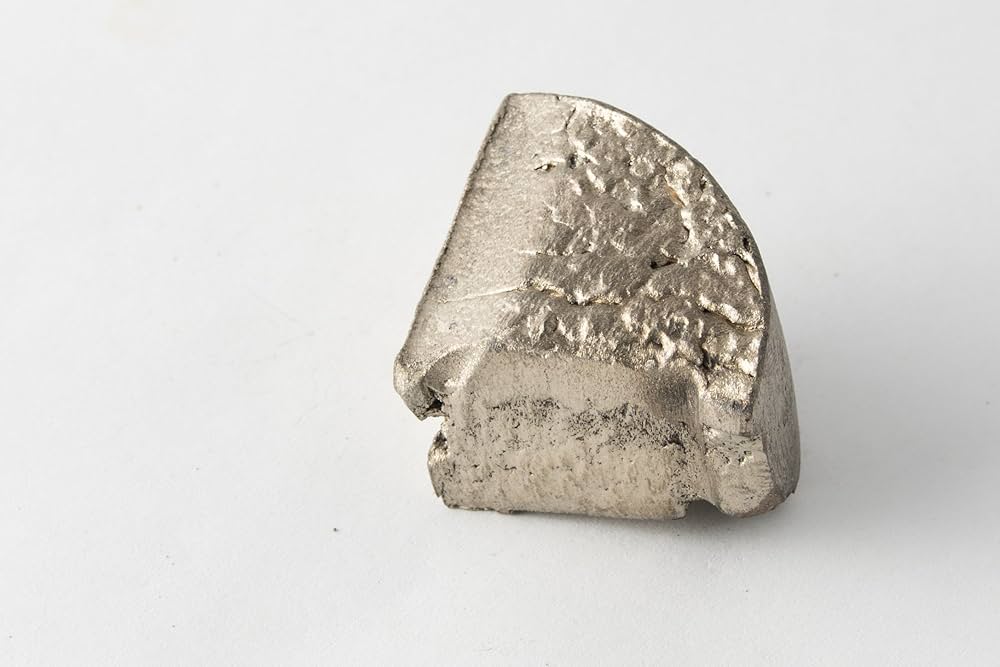
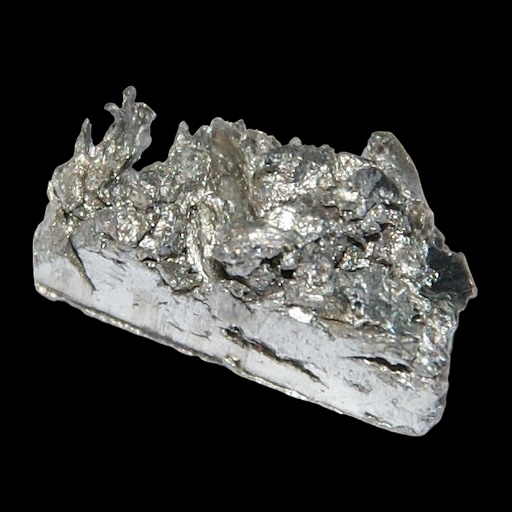
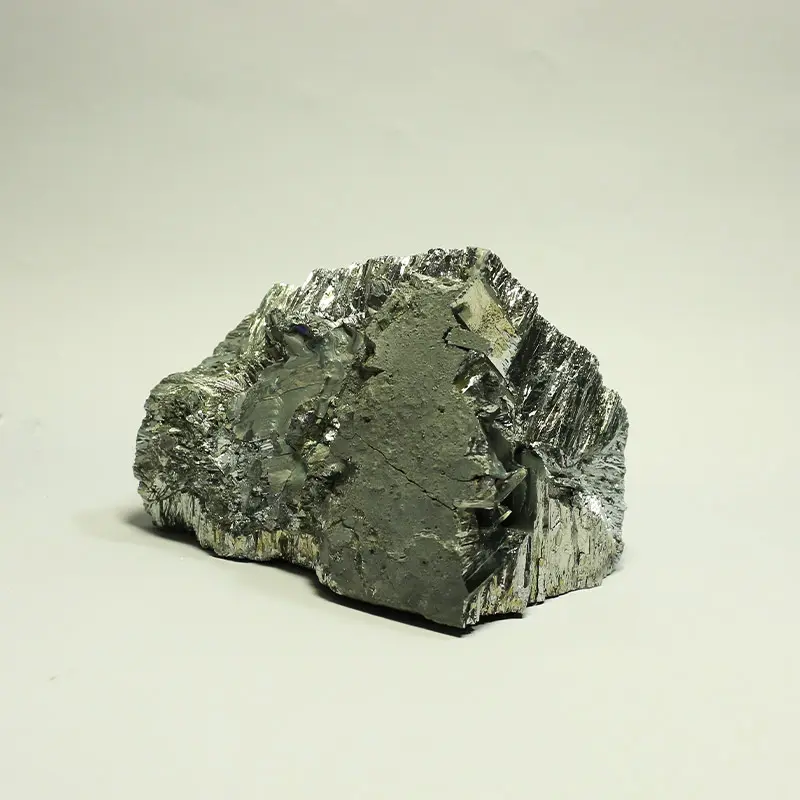
Ytterbium is a rare earth element that is part of the lanthanide series on the periodic table, denoted by the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. Discovered in 1878 by the Swedish chemist Jean Servais Stas, Ytterbium is named after the village of Ytterby in Sweden, which is known for its rich deposits of rare earth minerals. As a silvery-white metal, Ytterbium possesses unique physical and chemical properties that make it valuable in various applications, particularly in the fields of electronics, materials science, and medical technology.
One of the most notable uses of Ytterbium is in the manufacturing of high-performance materials, such as stainless steel and specialized alloys. When added to these materials, Ytterbium enhances their strength and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for demanding environments. In the realm of electronics, Ytterbium-doped materials are employed in solid-state lasers and optical devices, as they offer improved efficiency and performance over standard alternatives. Additionally, Ytterbium has found applications in the field of nuclear medicine, where it is used in certain imaging techniques and as a potential radiation therapy agent due to its stable isotopes.
Despite its promising applications, Ytterbium is relatively rare and can be challenging to extract and process. The mining of Ytterbium typically occurs in conjunction with other rare earth elements, often leading to environmental concerns due to the impact of extraction processes. Nonetheless, ongoing research and advancements in technology continue to explore new ways to utilize Ytterbium more effectively while minimizing environmental footprints. As global demand for high-tech materials and devices continues to grow, Ytterbium remains an essential player in the landscape of modern science and technology.