Description
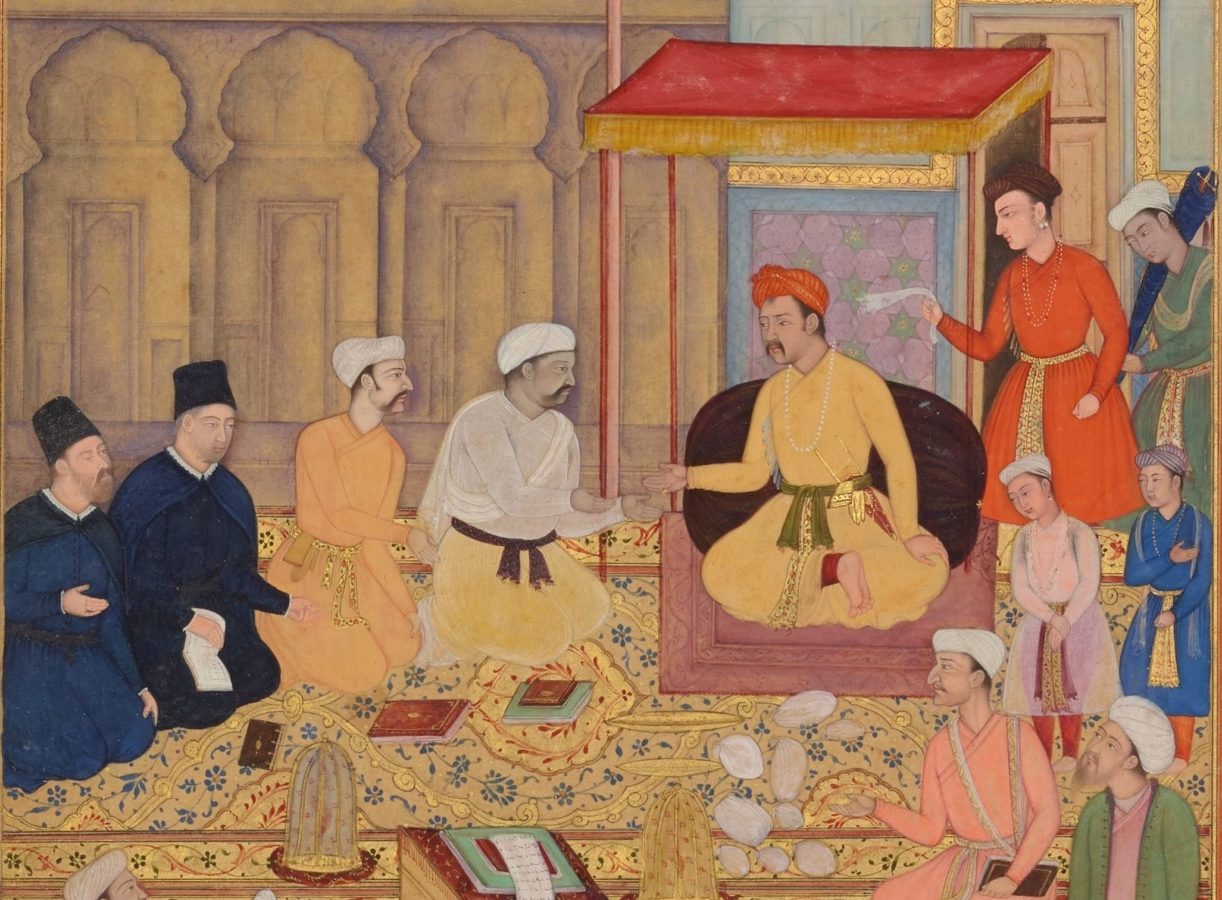
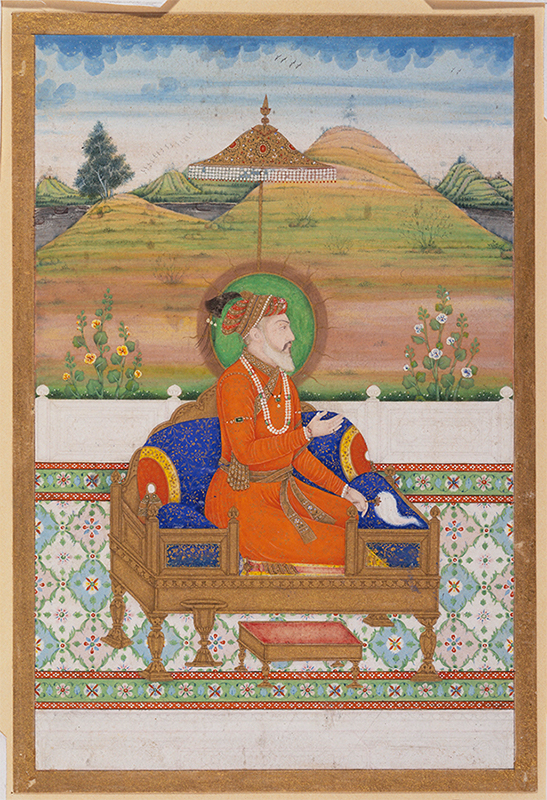
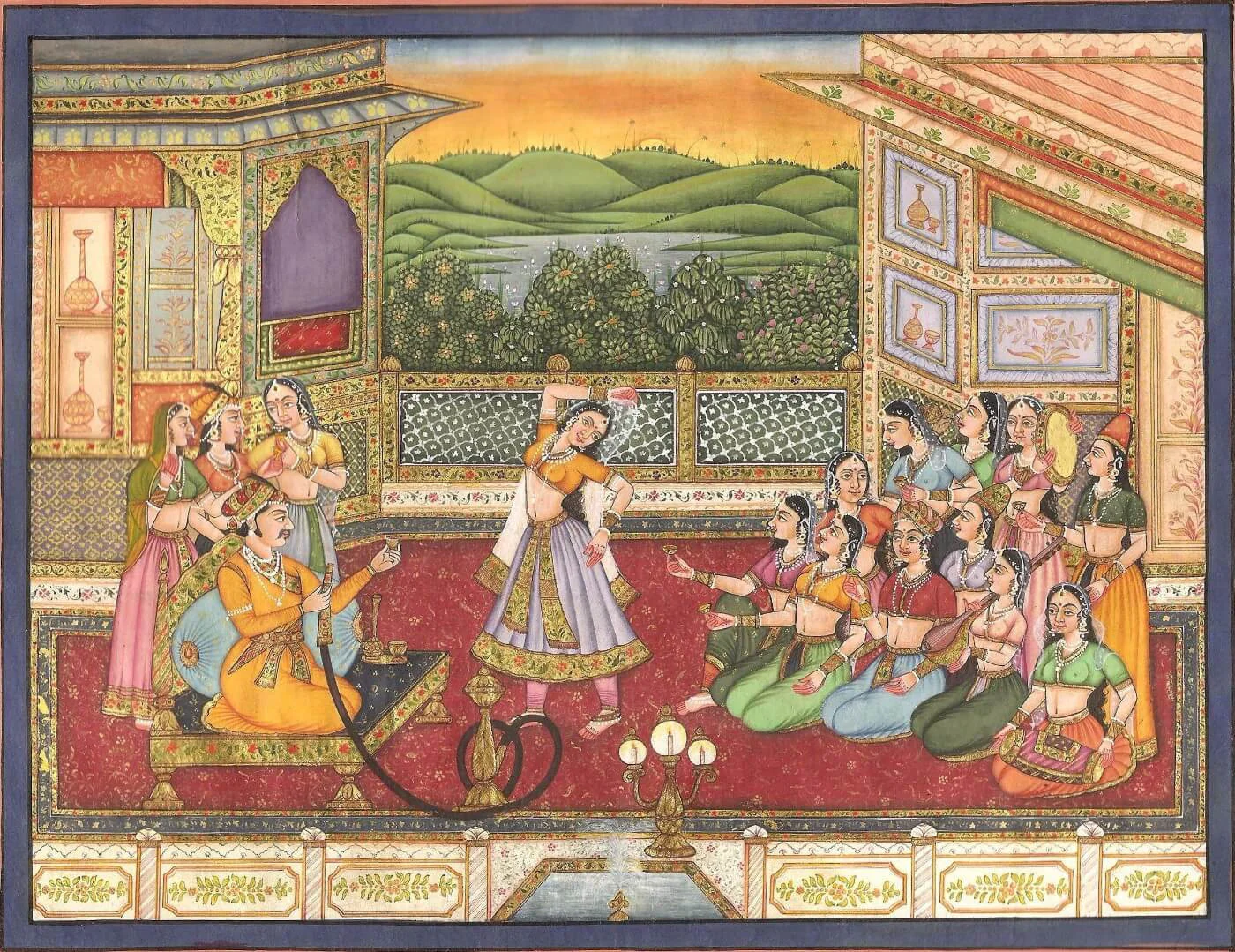
Mughal paintings refer to a style of miniature painting. They developed during the reign of the Mughal Empire from the 16th to the 18th century. The Mughals patronized painting, literature, and architecture. Mughal emperors established the tradition of miniature painting at their courts. Mughal paintings show a synthesis of Persian, European, and Indian styles. They are renowned for their brilliance of color, the delicacy of execution, and the fusion of artistic traditions. This style of miniature painting reached its artistic zenith under Akbar and Jahangir.
Mughal Painting is one of the essential topics for UPSC IAS Aspirants. It is a subpart of Art and Culture. Candidates preparing for UPSC will find it helpful.
History & Origin of Mughal Paintings
- The Delhi Sultanate reigned over most of the Indian subcontinent prior to the emergence of the Mughal Empire.
- Miniature painting has been developing in many places since the 10th century, and it flourished in numerous regional courts throughout the Sultanate of Delhi.
- When Humayun, the second Mughal emperor, returned from exile, he took two renowned Persian artists – Mir Sayyid Ali and Abd al-Samad – with him.
- These Persian artists created several notable paintings, notably the ‘Khamsa of Nizami,’ based on Humayun’s directions.
- These paintings strayed from traditional Persian art, resulting in the birth of a new art form known as ‘Mughal Painting.’ Subsequent Mughal kings expanded on the Mughal paintings.
- The Tutinama (‘Tales of a Parrot’) Painting is the first example of the Mughal style of painting